Why Upgrade to 12 Volts?
Upgrading your classic Ford 8N tractor from a 6-volt to a 12-volt electrical system offers significant advantages. The original 6-volt positive ground system, while functional in its time, suffers from limitations that become increasingly apparent with age. Dim headlights, a sluggish starter, and incompatibility with modern accessories are common complaints. A 12-volt negative ground system resolves these, providing a noticeably improved driving experience. But isn't this just a simple swap? No, this conversion requires careful planning and execution. Let's explore a comprehensive guide to ensure a safe and successful outcome. Have you considered the long-term benefits of increased reliability? For more in-depth information on Ford 8N engine rebuilds, check out this helpful resource: engine rebuild kits.
Getting Ready: Parts and Tools
Before starting, gather the necessary components and tools. This ensures a smooth workflow and minimizes interruptions. You will need:
- 12-Volt Battery: Select a battery appropriate for your tractor's size and mounting location. Ensure it's a 12-volt negative ground battery.
- 12-Volt Alternator: Choose an alternator compatible with your Ford 8N. Consider the amperage output to match your needs.
- 12-Volt Voltage Regulator: This critical component regulates the alternator's output voltage, preventing overcharging and damage to your electrical system.
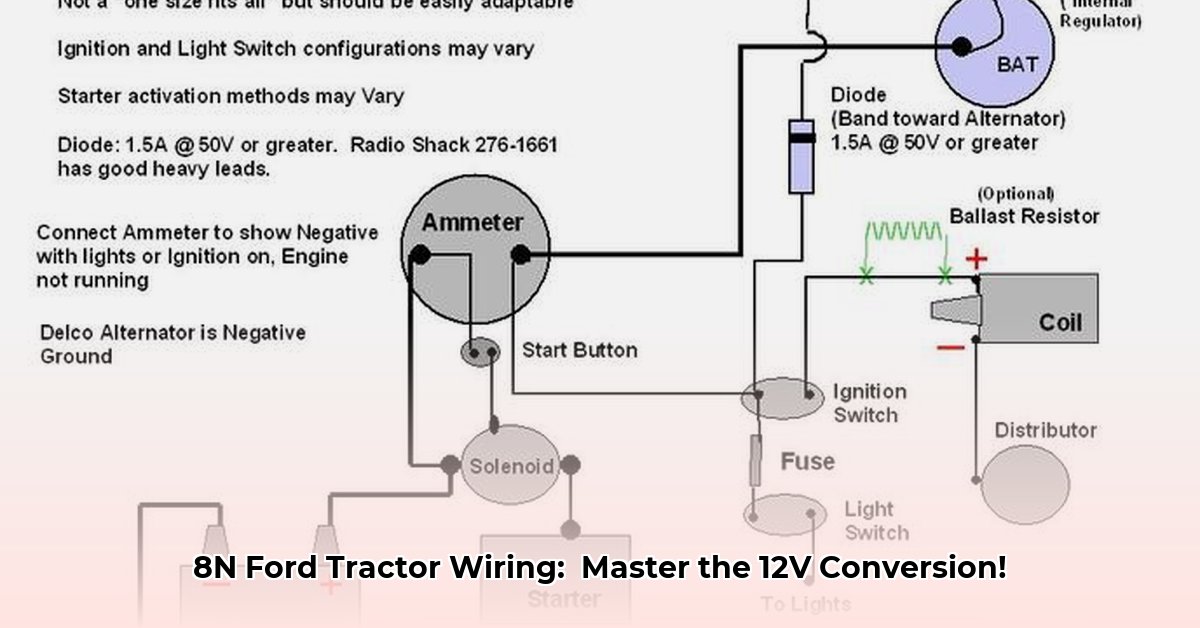
- Wiring Harness: A specifically designed 12-volt wiring harness is highly recommended. Modifying the existing harness is possible but significantly increases the risk of errors. Using a new harness ensures safety and correct wiring.
- 12-Volt Bulbs & Switches: Replace all existing 6-volt bulbs with their 12-volt counterparts. Similarly, consider updating switches.
- Tools: Basic hand tools such as screwdrivers (Phillips and flathead), pliers, wire strippers, crimpers, and a multimeter are essential. A good quality work light is also crucial.
The Conversion Process: A Step-by-Step Guide
This detailed guide walks you through each step of the 12-volt conversion. Remember: Always disconnect the battery's negative terminal before commencing any electrical work. This is a crucial safety precaution.
1. Assessing the Existing System: Begin with a thorough inspection of the existing 6-volt wiring. Document the current wiring layout using photos or a simple schematic. Identify all components – lights, starter motor, ignition coil, etc. – to understand their connections. This prevents unintentional damage during the conversion and allows for a more efficient replacement process.
2. Installing the New Battery: Securely mount the new 12-volt battery, ensuring correct polarity (+ and -). Double-check this; incorrect polarity can cause irreparable damage to electrical components and potentially cause a fire. Consult your tractor's manual for the correct battery size and location.
3. Installing the Alternator and Voltage Regulator: Mount the new alternator and voltage regulator securely. Their location varies depending on your tractor's specific model and configuration. Refer to your wiring harness instructions or consult a wiring diagram for optimal placement. Proper mounting is crucial for both their operation and to prevent damage during tractor use.
4. Installing the New Wiring Harness: This step is critical. Carefully follow the provided wiring diagram for your specific 12-volt harness. Connect each wire to its designated location. Double-check each connection before proceeding. Errors here can lead to short circuits, failed components, or worse. Taking your time and carefully verifying each connection is vital.
5. Testing the System: With the wiring complete, reconnect the battery (negative terminal last). Turn the ignition on and individually test all electrical components: headlights, taillights, turn signals, and the starter. Use your multimeter to verify proper voltage at key points. If any component malfunctions, retrace your steps and re-check all connections.
6. Final Checks and Adjustments: After thorough testing, conduct a brief test drive. Monitor all electrical components closely during operation.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
Even with careful preparation, problems can arise. Here's a guide to resolving common issues:
- Dim Lights: Check the alternator's output using your multimeter. A malfunctioning alternator or voltage regulator is a likely cause. Verify the connections to the bulbs themselves.
- Engine Won't Start: Verify all battery connections. Inspect the starter motor wiring and its connection to the battery. A faulty starter solenoid could also prevent the engine from starting.
- Electrical Short Circuits: Check for frayed or bare wires touching metallic parts. This can lead to fire and or damage. A multimeter can help pinpoint short circuits.
Weighing the Pros and Cons
A successful upgrade dramatically enhances your tractor's functionality and reliability. However, it requires a commitment to careful work and attention to detail.
| Advantage | Disadvantage |
|---|---|
| Improved starting power | Requires specialized knowledge and careful work |
| Brighter and reliable lights | Conversion cost can be significant |
| Compatibility with modern accessories | Potential voiding of original equipment warranties |
| Increased overall reliability | Potential for issues if not done correctly |
This conversion is a rewarding project, significantly improving your tractor’s performance and lifespan. However, remember that seeking professional help if you're unsure about any aspect of this project is always a smart choice. A successful conversion requires patience and a methodical approach.